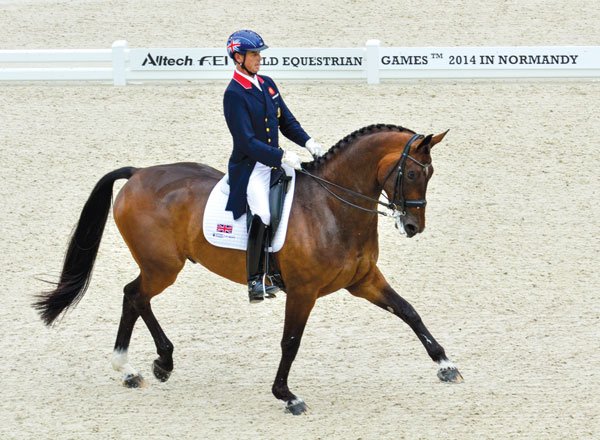
British Olympic gold medalist Carl Hester rides Nip Tuck with such steadiness and elasticity that you can sense the connection from the horse’s mouth right up to the rider’s elbow joints. Photo by Jennifer O. Bryant
Many equestrian disciplines require the horse to go on a loose rein, at least part of the time. But in dressage, there is a constant connection between the horse’s mouth and the rider’s hand, called contact.
Developing and maintaining correct contact can be one of the most difficult skills for dressage riders to learn. For a crash course, read on.
What Contact Isn’t
There are several common misconceptions about contact. Understanding what contact isn’t is almost as important as learning what it is. Contact is not:
◆ Pulling back or hanging on the reins, especially in an attempt to force a horse’s head and neck into a “frame.”
◆ Weightlessness in the hand. Although the horse is not supposed to lean on the rider’s hand as if it were a fifth leg, an empty rein is not the goal either. A dressage horse is supposed to become less dependent on the rein as he progresses through the levels, but contact is still present. “Lightness” is not necessarily correct!
◆ Manufactured by the rider. Yes, your reins have to be short enough for contact to happen, but it happens as a result of the horse’s forward energy. In other words, contact starts with the horse.
What Contact Is
So what is contact, then? Here’s the United States Dressage Federation (USDF) definition: The energy generated in the hindquarters by the driving aids must flow through the whole body of the horse and is received in the rider’s hands. The contact to the bit must be elastic and adjustable, creating fluent interaction between horse and rider with appropriate changes in the horse’s outline.
Contact is an element of the pyramid of dressage training, which depicts the classical dressage-training progression. The pyramid further explains that contact encompasses connection and acceptance of the bit through acceptance of the aids.
There is an old saying in dressage: Ride your horse “back to front” (from his hindquarters to the bit, or from your leg and seat into your hand), not “front to back.” That’s what the USDF definition and the pyramid language are getting at.
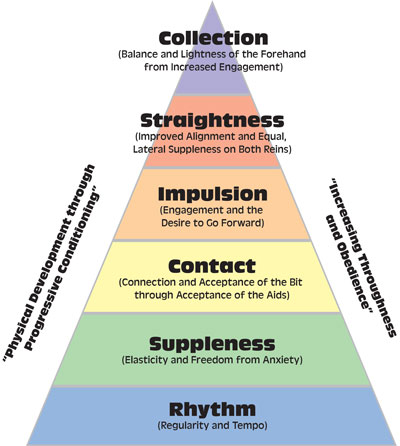
The dressage pyramid of training starts with rhythm as the most basic element. Training is actually an interplay of all of these qualities, but the levels of the pyramid suggest their progression. Note that contact is considered fairly fundamental. Photo used with permission from the United States Dressage Federation, www.usdf.org
Balance and Rebalance
There is no single training exercise that—presto!—will produce correct contact. But if I had to pick one thing to do (besides longe lessons, which teach the rider how to sit the horse’s gaits without using the reins for balance), it would be transitions, which develop your horse’s balance and his correct response to your forward-driving aids (your leg and seat).
Transitions between or within gaits teach your horse how to compress and lengthen his stride—to use himself like an accordion or to become adjustable. Walk-halt-walk. Walk-trot-walk. Trot-canter-trot. Walk-canter-walk. Or bigger trot-smaller trot-bigger trot. Smaller canter-bigger canter-smaller canter.
It’s easier to keep your horse balanced on curved lines, so practice transitions on a 20-meter circle before you try them on a straight line. Eventually, you’ll rebalance your horse by riding frequent micro-transitions—split-second, nearly invisible sequences in which you close your hand/give with the hand/use your leg to refresh the energy—known as half-halts.
What You Feel
As you progress in dressage, you’ll become more aware of your horse’s balance—which corresponds to how he feels in your hand. Is there dead weight in the reins pulling down and leaning on the bit? Try riding a transition that will shift weight off his forehand, followed by more energy from behind.
Do you have “empty reins” and you can’t see the bridle crownpiece when you glance down? Your horse may have curled his neck and is “hiding” behind the bit instead of reaching into the contact. This can be a tough habit to correct and may require a milder bit, help from an experienced trainer, or both.
A horse that snatches at the reins, pokes his nose up and out (goes “above the bit”), opens his mouth, sticks his tongue out of his mouth or over the bit, or exhibits other unwanted behaviors when asked to step forward into an elastic contact may be telling you that something hurts, that he feels trapped by your hand, or that he hasn’t been trained to accept the aids. A physical exam by your veterinarian is always a good first move, followed by a check of how well the tack fits, especially when it comes to the bit and bridle.
Once physical problems or discomfort have been ruled out, prepare for a slow, patient retraining process if you suspect that contact issues are the result of previous bad riding that caused pain in the mouth or general distrust of the rider’s hands.
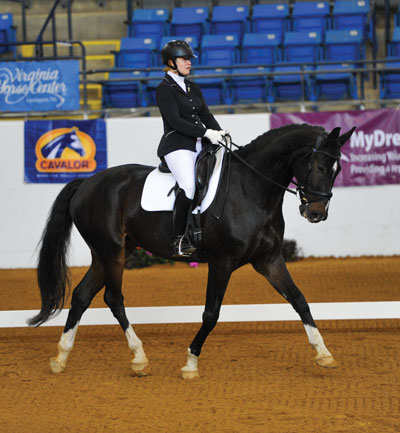

Here I am riding a medium trot at Second Level, in what appears to be an elastic and non-restrictive contact. My horse is stepping forward into the contact; it’s not being achieved by pulling back on the reins. Photo by PicsofYou.com
When the Reins “Come Alive”
Correct contact is described as elastic because the reins actually feel as if they’ve turned into nice big bungee cords, singing with energy and with an ideal amount of tension—neither taut nor slack.
Some people liken the feel to that of a firm-but-friendly handshake. Another analogy is the “alive” feeling of having a medium-sized fish on a line—which would feel different than a teensy goldfish that weighs next to nothing or a monster that’s threatening to pull you out of the boat.
Dressage is a conversation between horse and rider. When you start to sense that “alive” feeling in the reins, you’ll take your communication to a whole new level. n HI
This article about developing contact with your horse appeared in the August 2020 issue of Horse Illustrated magazine. Click here to subscribe!




